Anatomical Models
The MRISIMUL uses three different 3D computer models on which a pulse sequence is applied and the simulated images are calculated.
The simplest computer model is a user-defined phantom which is developed through a simple Graphical User Interface (GUI). This GUI allows the development of three-dimensional rectangular objects and assign to each of them unique MR characteristics.
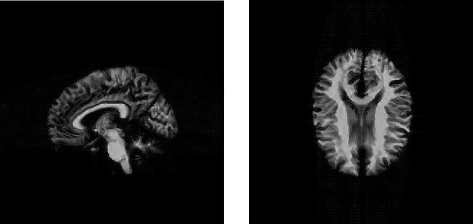
The second computer model is a brain anatomical model available online by the McConnell Brain Imaging Center at McGill University (Montreal, Canada). This computer model is a three-dimensional digital brain phantom that described the “fuzzy” spatial distribution of 11 different tissue types.
The third computer model is a detailed three-dimensional computer model of the anatomy of the human heart which developed in our lab based on the dataset of high resolution images provided by the Visible Human Project (VHP) of the United States National Library of Medicine (Bethesda, MD).